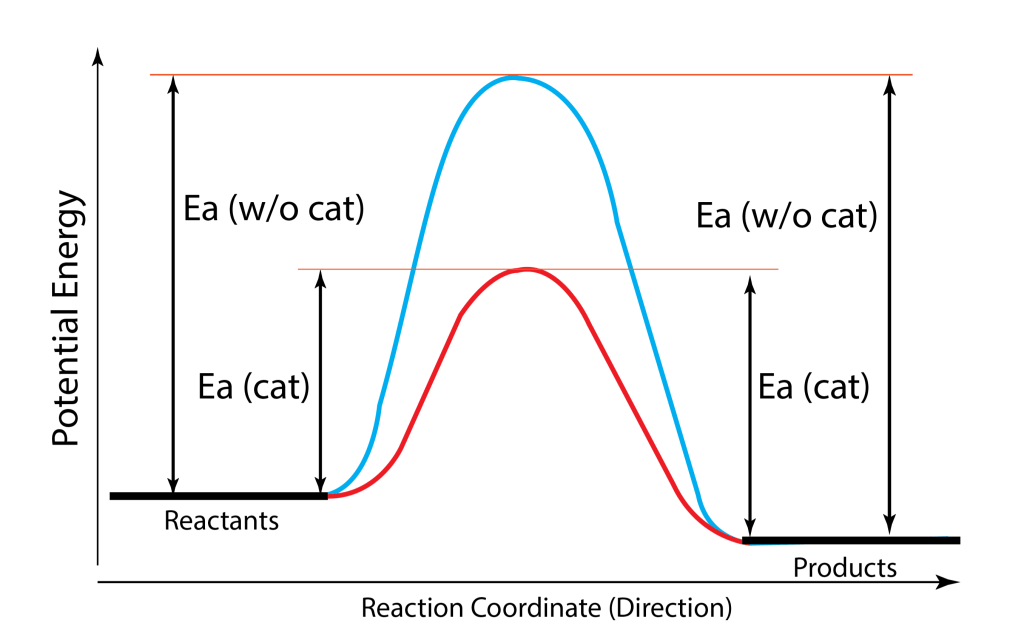
A catalyst is a special molecule that promotes the completion of a specific reaction. Biological catalysts are called enzymes. A catalyst lowers the energy required for a reaction to occur, making it closer to ambient conditions. In case of RESR technology, the catalyst helps to transfer a hydride and proton and combine them into H2. Normally thermal dehydrogenation of ammonia occurs at 130 °C. However, the UCD patented catalyst promotes dehydrogenation at 20 to 25°C, thus the same reaction occurs, but requiring less energy.