
Ammonia borane (AB) is a hydrogen rich molecule with the potential to release high amount of H2 per mass. Moreover, AB contains both a hydric H (attached to B) and a protonic H (attached to N). The cleanest method to release H2 is to combine these two types of hydrogen, while keeping the temperature as close to ambient conditions. To perform this operation, a specific type of molecule, a catalyst is required. A catalyst keeps to speed up a reaction while maintaining its structure through several million cycles. Read about catalysts here.
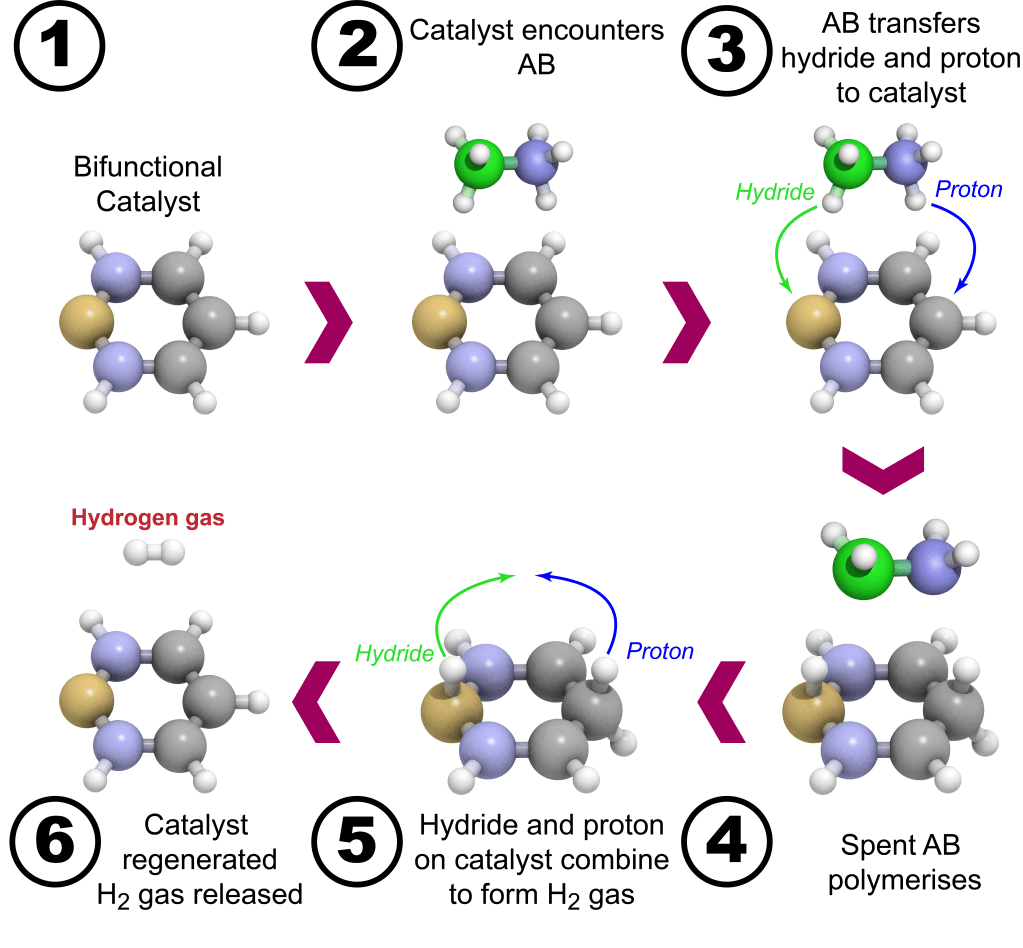
The RESR catalyst was designed, synthesised and tested by the Phillips groups at the school of chemistry at University College Dublin. Both 1st and 2nd generation of catalyst were patented and published here. The Ru-based catalyst is a specifically designed bifunctionally active compound, where both the metal and ligand are active to transfer hydrogen from ammonia borane. The simplified mechanism of the catalyst is shown below. The catalyst is special in that both a hydride and proton are transferred simultaneously to the catalyst. The catalyst then recombines the hydride and proton to form a high purity stream of hydrogen gas. The mechanism was computationally model and can be read here and here.
A video showing the early testing of the UCD bifunctional catalyst for ammonia borane dehydrogenation in the laboratory can be viewed below.
In order to move from the laboratory to a standalone device, an enclosed reactor system was designed and built. It features an impeller for high speed mixing, an injection system controlled by a programmable microcontroller, a H2 release valve, a storage vessel. The reactor is connected to a commercial 100 W proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEM-FC) supplied by Horizon Education.

Photographs of the initial testing of the reactor with the catalyst, showing dehydrogenation of the ammonia borane.
The diagram below shows the two sides of the technology. Onboard dehydrogenation of ammonia borane by the catalyst to supply high purity H2 for a PEM fuel cell. Then off-board regeneration of the spent AB through a two step process.

Goto the Team page
